
Value vs Growth Stocks Performance Review
On the other hand, growth stocks represent companies with above-average earnings growth potential. They usually reinvest earnings into expansion and innovation. Growth stocks attract investors aiming for capital appreciation over time.
Understanding these strategies is vital for investors as they dictate the choice of stocks within a portfolio and align with individual financial goals and risk tolerances.
1. Value Stocks
Definition and Characteristics of Value Stocks
Value stocks are shares in companies that considered undervalued by the market. These stocks typically have low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, low price-to-book (P/B) ratios, and high dividend yields. They are often associated with well-established, mature companies in traditional industries. Investors are usually drawn to value stocks for their potential for long-term capital appreciation, stability, and dividend income. A key characteristic of value stocks is their perceived safety in turbulent markets, making them an attractive option for risk-averse investors.Historical Value Stocks Performance and Successful Examples
Value stocks have a solid performance history, often outperforming growth stocks during specific market conditions. Notable examples include blue-chip companies like Coca-Cola and Johnson & Johnson, which consistently generate dividends and exhibit steady growth. Historical data shows that value stocks excel during economic downturns or when markets favor stable, income-generating investments. Investors often turn to value stocks for stability and long-term value appreciation.Investment Strategies for Value Stocks
- Fundamental Analysis
This approach entails deeply examining a company's financial health, including earnings, cash flow, and balance sheets. Value investors search for stocks trading below their intrinsic value, aiming to buy them at a discount. Fundamental analysis helps identify such opportunities and assess the long-term potential of value stocks in a portfolio. - Dividend Yield and Income Generation
Investment strategies for value stocks often focus on dividend yield and income generation. Investors seek out companies with solid fundamentals, stable cash flows, and a history of consistent dividend payments. These stocks provide a source of regular income, making them appealing to income-oriented investors. Additionally, reinvesting dividends can accelerate wealth accumulation over the long term, enhancing the value stock strategy's effectiveness.
Risks Associated With Investing in Value Stocks
Investing in value stocks presents certain risks. One major concern is the potential for value traps, where a stock's low price may indicate underlying issues rather than undervaluation. Economic downturns can further dampen value stocks' performance. Additionally, these stocks have limited growth potential compared to growth stocks. A lack of market interest could result in extended periods of underperformance, affecting portfolio returns.Real-World Case Studies of Value Stock Investments
Value stocks are shares of companies undervalued by the market, often trading at lower price-to-earnings ratios and offering solid dividend yields. These stocks are usually associated with established, mature companies. Investors interested in value stocks often perform fundamental analysis to identify such opportunities. Real-world case studies, like the success stories of Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway and Benjamin Graham's investments, demonstrate how investing in undervalued companies with strong fundamentals can yield substantial returns over time.
The Best Free Investment You’ll Ever Make
Join Wealth Daily today for FREE. We’ll keep you on top of all the hottest investment ideas before they
hit Wall Street. Become a member today, and get our latest free report: “Why You Need to Fire Your Money
Manager.”
It contains full details on why money managers are overpaid and provides you with
tools for growing your wealth.On your own terms. No fees, no commission.
We never spam!
View our Privacy Policy
After getting your report, you’ll begin receiving the Wealth Daily e-Letter, delivered to your inbox
daily.
2. Growth Stocks
The Best Free Investment You’ll Ever Make
Join Wealth Daily today for FREE. We’ll keep you on top of all the hottest investment ideas before they
hit Wall Street. Become a member today, and get our latest free report: “Why You Need to Fire Your Money
Manager.”
It contains full details on why money managers are overpaid and provides you with
tools for growing your wealth.On your own terms. No fees, no commission.
Definition and Characteristics of Growth Stocks
Growth stocks are equities associated with companies expected to expand at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market. These stocks typically exhibit strong revenue and earnings growth, often reinvesting profits into the business for expansion rather than paying dividends. Investors seek growth stocks for the potential of substantial capital appreciation, although they often come with higher volatility and valuations reflecting future growth expectations.Historical Growth Stocks Performance and Successful Examples
Growth stocks have a history of delivering impressive performance, often characterized by substantial capital appreciation. Companies like Amazon, Apple, and Tesla exemplify the success of growth stocks, with their shares consistently outpacing broader market indices. These stocks tend to prioritize reinvestment and innovation, which can lead to remarkable long-term gains for investors. Understanding the historical successes of growth stocks is essential for those considering them as part of their investment strategy.Investment Strategies for Growth Stocks
- Focusing on Future Potential and Innovation
Investors targeting growth stocks prioritize companies poised for substantial future expansion. This strategy emphasizes identifying innovative firms with disruptive technologies or products. It involves researching a company's long-term growth prospects, assessing its competitive advantage, and considering market trends and leadership factors. Investment in growth stocks typically involves a willingness to tolerate higher volatility in exchange for the potential for significant capital appreciation as these companies continue to grow and capture market share. - Understanding Growth Metrics
This involves analyzing revenue growth rates, earnings projections, and market share expansion. By evaluating these metrics, investors can gauge the potential of a company's future growth trajectory and make informed decisions. However, they must also be cautious of the associated risks, as growth stocks can be more volatile and subject to market sentiment shifts.
Risks Associated With Investing in Growth Stocks
Investing in growth stocks can be lucrative but comes with inherent risks. These stocks often have high valuations, making them vulnerable to market corrections. Additionally, their success hinges on sustained rapid growth, making them sensitive to economic downturns. Newer companies might need a proven track record, increasing uncertainty. Furthermore, growth stocks are usually affected by shifts in investor sentiment, causing volatile price swings. Diversification and careful research are essential to mitigate these risks when considering growth stock investments.Real-World Case Studies of Growth Stock Investments
Growth stocks, characterized by their potential for substantial capital appreciation, have yielded remarkable success stories. One such instance is Amazon's meteoric rise from an online bookstore to a global e-commerce and tech giant. Similarly, Tesla's innovative electric vehicles positioned it as a leader in sustainable transportation, driving its stock price to unprecedented heights. These case studies underscore the potential rewards and inherent risks of investing in growth stocks.3. Factors Influencing the Choice Between Value vs Growth Stocks
Investor's Risk Tolerance and Investment Goals
Investors' risk tolerance and investment goals are pivotal in deciding between value vs growth stocks. Risk-seeking investors with a longer horizon favor growth stocks for potential capital appreciation, while risk-averse ones seeking stability and income lean towards value stocks. Balancing these factors with market cycles, interest rates, and industry trends is crucial for a well-informed investment strategy.Economic and Market Cycles
During periods of economic expansion, growth stocks thrive due to their potential for rapid earnings growth. Conversely, value stocks might perform better during market downturns as investors seek stability and dividends. Understanding these cycles and their impact on investment styles helps investors tailor their portfolios to align with prevailing market conditions.Value vs Growth Stocks Performance – Interest Rates and Inflation
Interest rates and inflation play a crucial role in the value-growth stock decision. When interest rates are low, growth stocks shine due to their future potential, while value stocks might underperform. In contrast, value stocks often perform better during high inflation as their stable cash flows and dividends gain prominence. Investors must consider these economic factors, risk tolerance, and market cycles to make informed choices between these investment approaches.Industry Trends and Innovations
Industry trends and innovations significantly influence investors' decisions between value and growth stocks. The potential for growth stocks to thrive in dynamic sectors, such as technology and biotech, can attract those seeking substantial returns. On the other hand, value stocks appeal to those looking for stability in more mature industries. Assessing these trends and innovations alongside personal risk tolerance and market cycles is crucial when determining the optimal investment strategy.4. Value vs Growth Stocks Performance – Which Strategy Is Right for You?
Assessing Your Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
Determining the right investment strategy between value vs growth stocks hinges on a critical self-assessment. Start by clearly defining your financial goals, whether long-term wealth accumulation or short-term gains. Equally important is gauging your risk tolerance – your comfort level with market fluctuations. Value stocks suit you if you seek steadiness and can withstand market volatility. Conversely, growth stocks might be better if you're after high growth potential and can tolerate more risk. Finding alignment between your goals and risk appetite is essential for sound investment decisions.The Role of Value vs Growth Stocks in a Diversified Portfolio
Value stocks, typically stable and income-focused, suit conservative investors seeking reliable dividends and less volatility. In contrast, growth stocks cater to those with a longer time horizon, craving potential high returns through capital appreciation, though with higher risks. A balanced approach is often advisable, blending both strategies in a diversified portfolio. This blend offers stability and growth potential, aligning with varied financial objectives and ensuring resilience in diverse market conditions, ultimately optimizing the risk-reward balance for investors.Strategies for Combining Value vs Growth Stock Investments
The best investment strategy between value and growth stocks is usually chosen depending on a person's financial goals and risk tolerance. Conservative investors looking for steady, dividend-paying investments willing to wait for possible appreciation can consider value equities. Growth stocks, which seek quick cash gains in cutting-edge industries, draw investors with a higher risk tolerance. A well-balanced strategy, though, might offer the best of both worlds. A diversified portfolio that combines value and growth investments reduces risk while maximizing potential gains. Assessing personal objectives and risk tolerance is essential because the appropriate blend differs for every investor.Expert Opinions and Investment Advisor Insights
Expert opinions and insights from seasoned investment advisors can be invaluable. These professionals can help individuals assess their financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment time horizons, providing tailored recommendations. They often advocate for a diversified approach that combines elements of both strategies, offering a balanced portfolio. Ultimately, their guidance is crucial in helping investors align their chosen strategy with their unique circumstances, ensuring a more informed and potentially successful investment journey.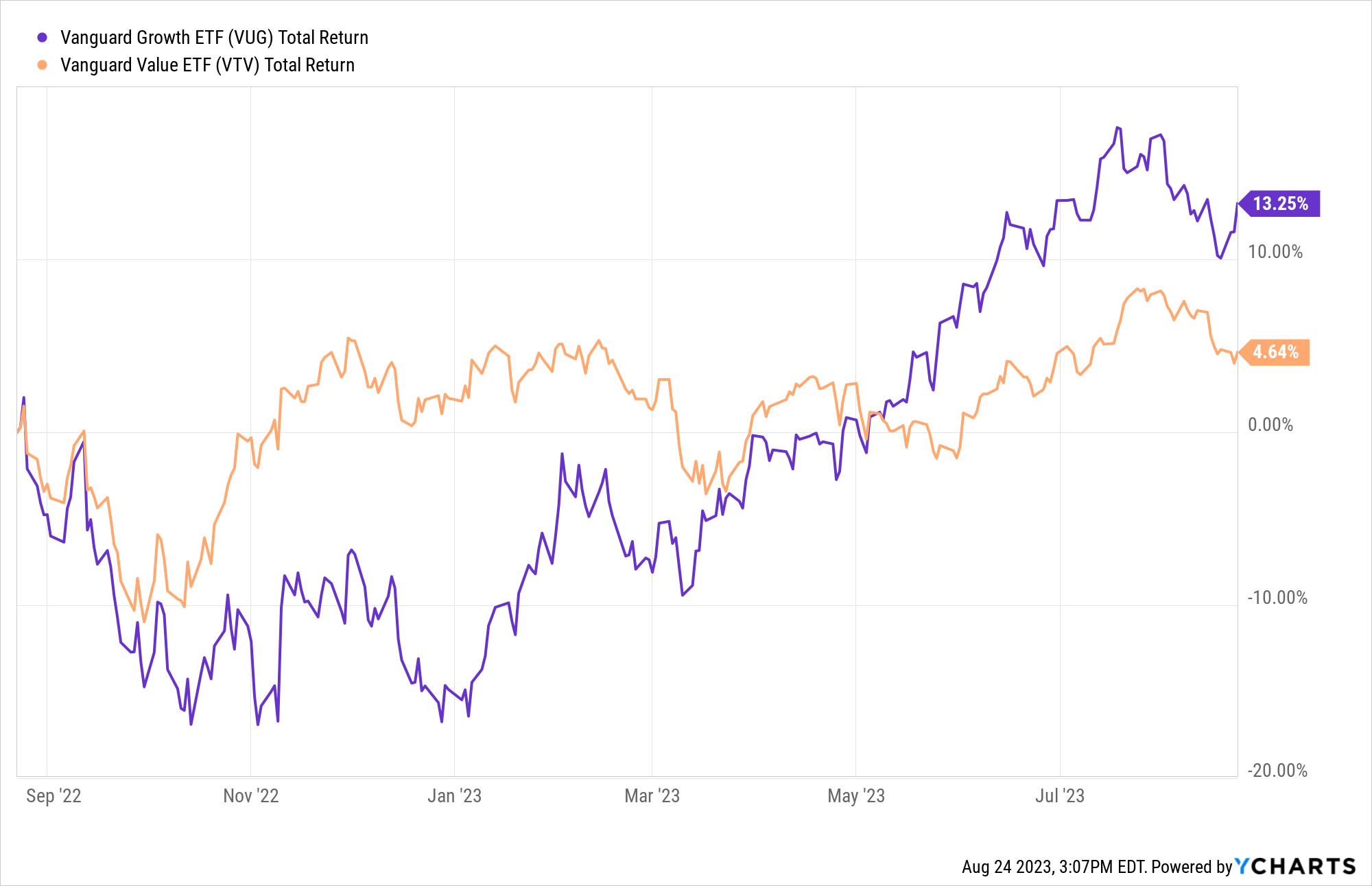
A 1-Year Look at Vanguard Value ETF vs Vanguard Growth ETF (Total Return)


